Business process management (BPM)
What is BPM?
Business process management (BPM) is a methodology to manage processes and workflows in an organization. The goal of BPM is to increase efficiency, performance, and agility in the day-to-day operations of a business. BPM has been widely adopted by organizations and is essential for any enterprise businesses that want to be competitive in today’s marketplace.
Watch this video to learn about Pega’s case management software and how it can empower your organization to efficiently manage complex business processes.
Why is BPM important?
BPM helps simplify and automate operations so you can reduce costs and improve business agility. By using BPM, organizations create repeatable solutions that can be efficiently reused and tailored to meet the requirements of diverse users, product lines, channels, and geographies.
Benefits of BPM
BPM drives efficiency in several ways:
- Cost reduction and operational agility: BPM simplifies and automates operations, unlocking avenues for substantial cost cuts.
- Repeatable solutions: Using BPM helps create efficient, scalable, and adaptable solutions.
- Streamlined workflows: BPM identifies and optimizes processes, reducing redundancies and removing bottlenecks.
- Enhanced user experience: BPM reduces tedious tasks and improves accuracy, which translates to fewer mistakes and a better overall experience for customers and employees.
- Structured service delivery: BPM creates a structured environment, reducing response times and enabling faster customer service.
It’s more than just operational enhancements. BPM shapes a responsive, cost-effective, and user-friendly organizational landscape. By integrating BPM, you can position yourself to thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.

How does BPM work?
BPM uses a combination of technologies – including workflow automation, AI-powered decisioning, and case management – to build comprehensive solutions for organizations. By leveraging these technologies, organizations improve business processes that enable them to bring products to market faster; make, market, and sell more profitably; and deliver superior customer service.

Relationship between BPM and automation
BPM and business process automation (BPA) form a symbiotic relationship at the heart of efficient organizations. Together, they create a dynamic synergy, streamlining operations, reducing errors, and enhancing overall performance. To break down the distinctions between BPM and BPA:
BPM
- Overarching strategy
- Defines, models, and optimizes business processes
- Identifies areas in a workflow that can benefit from automation
BPA
- Execution arm of BPM
- Utilizes technology to automate processes
- Actualizes BPM's identified enhancements
- Ensures that routine, rule-based tasks are executed seamlessly, freeing up human resources for more strategic, creative, and complex endeavors
Use cases for BPM
Discover how businesses across industries use BPM to transform the way work gets done.
Financial services
Banco Santander Basil has utilized BPM to significantly enhance its client services. By adopting BPM methodologies, the bank has optimized its service delivery processes, thereby reducing response times, minimizing errors, and improving overall customer satisfaction.
Healthcare
Highmark Health showcases the versatility of BPM by applying it to create innovative, patient-centered solutions. By focusing on process optimization, Highmark Health has been able to enhance service quality, streamline administrative tasks, and ultimately provide better care to its patients.
Travel & hospitality
By harnessing the capabilities of BPM, Booking.com can efficiently manage a vast array of traveler interactions and streamline its customer service processes. This approach enables them to maintain a robust platform where reservations, inquiries, and customer interactions are handled swiftly and seamlessly.
Different types of BPM
BPM isn’t one-size-fits-all—different types have evolved to meet a range of organizational goals and challenges.
Integration-centric BPM
Integration-centric BPM targets processes with minimal human involvement, relying on APIs for efficient data integration, as seen in HRM or CRM systems.
Human-centric BPM
Human-centric BPM focuses on processes requiring human interaction and approvals, offering intuitive interfaces for task assignments and accountability.
Document-centric BPM
Document-centric BPM addresses documentation processes. From creation and review to approval and storage, BPM streamlines everything involved with business-critical documents, which makes it easier to accomplish tasks such as formalizing intricate contracts or ensuring data privacy.
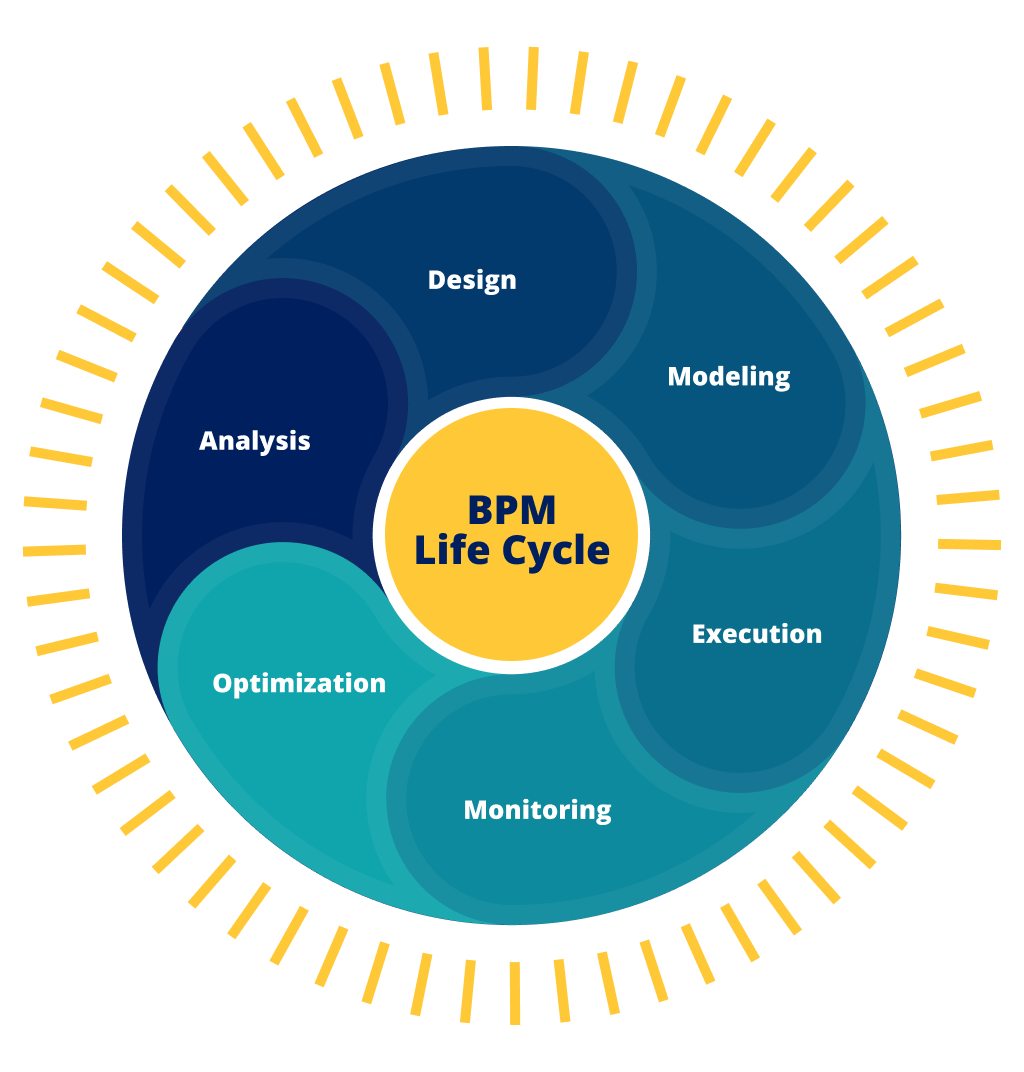
Understanding the BPM Lifecycle
To effectively implement BPM, it's essential to understand its lifecycle—a structured approach that guides how processes are identified, designed, executed, and improved over time. Each stage plays a critical role in building efficient, scalable, and adaptive business operations.
- Analysis: Discover and identify processes and workflows that can be created or optimized to meet business requirements or improve performance.
- Design: Create process designs that include human-to-human, system-to-system, or human-to-system interactions. Designs should aim to reduce errors and maintain relevant operating procedures or SLAs.
- Modeling: Use software tools to effectively model and evaluate process designs. Once a process design is ready, use varying input values to observe its behavior. If undesirable behavior is observed, make design changes iteratively.
- Execution: Automate processes with business rules, decisioning, case management, and other related technologies.
- Monitoring: Leverage reporting data collected from processes for performance, errors, and compliance. Monitoring allows businesses to evaluate executed BPM solutions against corresponding design models and relevant KPIs.
- Optimization: Leverage data from the modeling and monitoring phases to identify areas of the solution that can be improved to derive higher efficiency and better value.
BPM components
Key components of BPM enable smarter, faster, and more consistent operations.Turns intelligence into action by tapping into data, analyzing the current need, and providing the best response at that moment.
Uses AI to predict customer needs, personalize interactions, and streamline experiences across channels.
Manages complex human and machine work from start to finish with a case used as the epicenter to manage tasks and outcomes.
Automates complicated processes. Setting rules puts goals into action within a business application.
Makes statistics available that you can analyze in comprehensible reports to improve your business.
Provides a framework for safeguarding against unauthorized access. Prevents attacks that compromise performance and availability.
Access data across any application with broad and flexible connectors, adaptors, and API services.

BPM challenges and strategic solutions
The implementation of modern BPM systems continues to face several persistent challenges, but the solutions are becoming more sophisticated and strategic.
- Implementation complexity can be a BPM hurdle. A gradual rollout—starting with pilot projects—can help teams build confidence, show value, and reduce risk before scaling across the organization.
- Change management can be a major challenge, with employees often resisting new processes. Success will depend on clear communication, strong training, and cross-functional teams that prioritize adoption and usability.
- Technology integration can be challenging but can be eased by flexible BPM platforms that support analysis, automation, and improvement. Modern solutions like Pega's unified platform can help to unify systems, breaking down silos and enabling seamless connectivity across processes and channels.
Enhancing BPM with agentic AI
Agentic AI enhances BPM by enabling systems to understand goals, plan and execute actions autonomously, and adapt to change. Unlike rule-based automation, it perceives context, reasons through complexity, makes decisions, and learns from experience. This creates intelligent, resilient, and self-optimizing processes that deliver agility and strategic value with minimal human input. Pega Blueprint brings this vision to life by providing a model-driven approach to designing agentic workflows that align business goals with adaptive, AI-powered execution.
The future of BPM: The rise of agentic workflows
As the landscape BPM continues to evolve, one of the most significant trends observed is the shift towards agentic workflows. These workflows are powered by AI agents capable of autonomously managing tasks, making decisions, and adapting to changing conditions—all while remaining aligned with strategic human oversight. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, agentic workflows are dynamic, context-aware, and capable of learning from interactions. This enables businesses to move beyond rigid process automation toward more intelligent, flexible, and scalable operations.