ビジネスプロセス管理(BPM)
BPMについて
ビジネスプロセス管理(BPM)とは、組織のプロセスとワークフローを管理する手法です。BPMの目的はビジネスの日常業務の効率、パフォーマンス、アジリティを向上させることです。BPMは多くの組織で広く採用されており、今日の市場で競合性を高めたいエンタープライズビジネスには不可欠です。
この動画では、Pegaのケースマネージメントソフトウェアについて、また、それがどのように組織を強化し、複雑なビジネスプロセスを効率的に管理するのに役立つかをご紹介します。
BPMが重要な理由
BPMはお客様の業務を簡素化および自動化します。これによりコストを削減し、ビジネスのアジリティが向上します。BPMを使用して、組織はさまざまなユーザー、製品ライン、チャネル、地域などの要件に合うように効率的な再利用や調整ができる、繰り返し可能なソリューションを創出します。
BPMのメリット
BPMはいくつかの点で効率化を促進します。
- コスト削減と業務のアジリティ:BPMにより、業務が簡素化および自動化され、大幅なコスト削減の道が開かれます。
- 繰り返し可能なソリューション:BPMを使用すると、効率性、拡張性、適応性の高いソリューションを創出できます。
- ワークフローの簡素化:BPMはプロセスを特定および最適化し、冗長性を軽減してボトルネックを取り除きます。
- ユーザーエクスペリエンスの強化:BPMによりボトルネックが排除され、面倒なタスクが減り、精度が向上します。結果としてミスが減り、顧客と従業員の体験が全体的に向上します。
- サービス提供の構造化:BPMによって構造化された環境が構築され、応答時間が短縮されるため、迅速なカスタマーサービスを実現できます。
単なる業務改善にとどまりません。BPMは、応答性が高くコスト効率に優れた、ユーザーフレンドリーな組織環境を形作ります。BPMを統合すれば、進化し続ける市場で成功するための態勢を整えることができます。

BPMの仕組み
BPMは、ワークフローの自動化、AIを活用した意思決定、ケースマネージメントなどのテクノロジーを組み合わせて、組織向けの包括的なソリューションを構築します。これらのテクノロジーを活用することで、組織はビジネスプロセスを改善して製品を迅速に市場に投入し、製造、マーケティング、販売の収益性を高め、優れたカスタマーサービスを提供できるようになります。

BPMとオートメーションの関係性
BPMとビジネスプロセスの自動化(BPA)によって、効率的な組織の中心に共生関係が形成されます。組み合わせることで動的な相乗効果が生まれ、業務の簡素化、エラーの削減、パフォーマンス全体の向上を実現します。BPMとBPAの特徴は、それぞれ次のとおりです。
BPM
- 包括的な戦略
- ビジネスプロセスを定義、モデル化、最適化
- オートメーションによってメリットが得られるワークフロー内の領域を特定
BPA
- BPMにとって実行部門に該当
- テクノロジーでプロセスを自動化
- BPMによる改善を具体化
- ルーチン作業とルールベース作業を円滑に実行し、人的資源をより戦略的かつ創造的で複雑な業務に活用
BPMの導入事例
さまざまな業界で企業がBPMを活用し、仕事の進め方を変革している事例をご覧ください。
金融サービス
Banco Santander Basilは、BPMを活用してクライアントサービスを大幅に向上させています。BPM手法を採用することで、サービス提供プロセスを最適化し、応答時間の短縮、エラーの最小化、全体的な顧客満足度の向上を実現しています。
ヘルスケア
Highmark Healthは、BPMを応用して革新的な患者中心のソリューションを創出することで、その汎用性を実証しています。プロセスの最適化に注力することで、Highmark Healthはサービス品質を高め、管理業務を簡素化し、最終的には患者に対するケアの質を高めることができました。
旅行とホスピタリティ
Booking.comはBPMの機能を活用することで、旅行者とのさまざまなやり取りを効率的に管理し、カスタマーサービスプロセスを合理化しています。このアプローチにより、堅牢なプラットフォームを維持し、予約、問い合わせ、顧客対応を迅速かつシームレスに処理できるようになりました。
さまざまなタイプのBPM
BPMは汎用的なものではなく、さまざまなタイプが組織の幅広い目標と課題に対応するために進化してきました。
統合中心のBPM
統合中心のBPMは、HRMシステムやCRMシステムに見られるような効率的なデータ統合を実現するAPIを使用して、人間の関与を最小限に抑えたプロセスを目標にします。
人間中心のBPM
人間中心のBPMは、人間によるインタラクションと承認を必要とするプロセスに焦点を当てており、タスクの割り当てと説明責任に直観的なインターフェイスを提供します。
ドキュメント中心のBPM
ドキュメント中心のBPMは、ドキュメントプロセスに対応します。作成や確認から承認、保存まで、BPMはビジネスに不可欠なすべてのドキュメント関連作業を合理化します。複雑な契約の形式化やデータプライバシーの確保など、タスクの完了が容易になります。
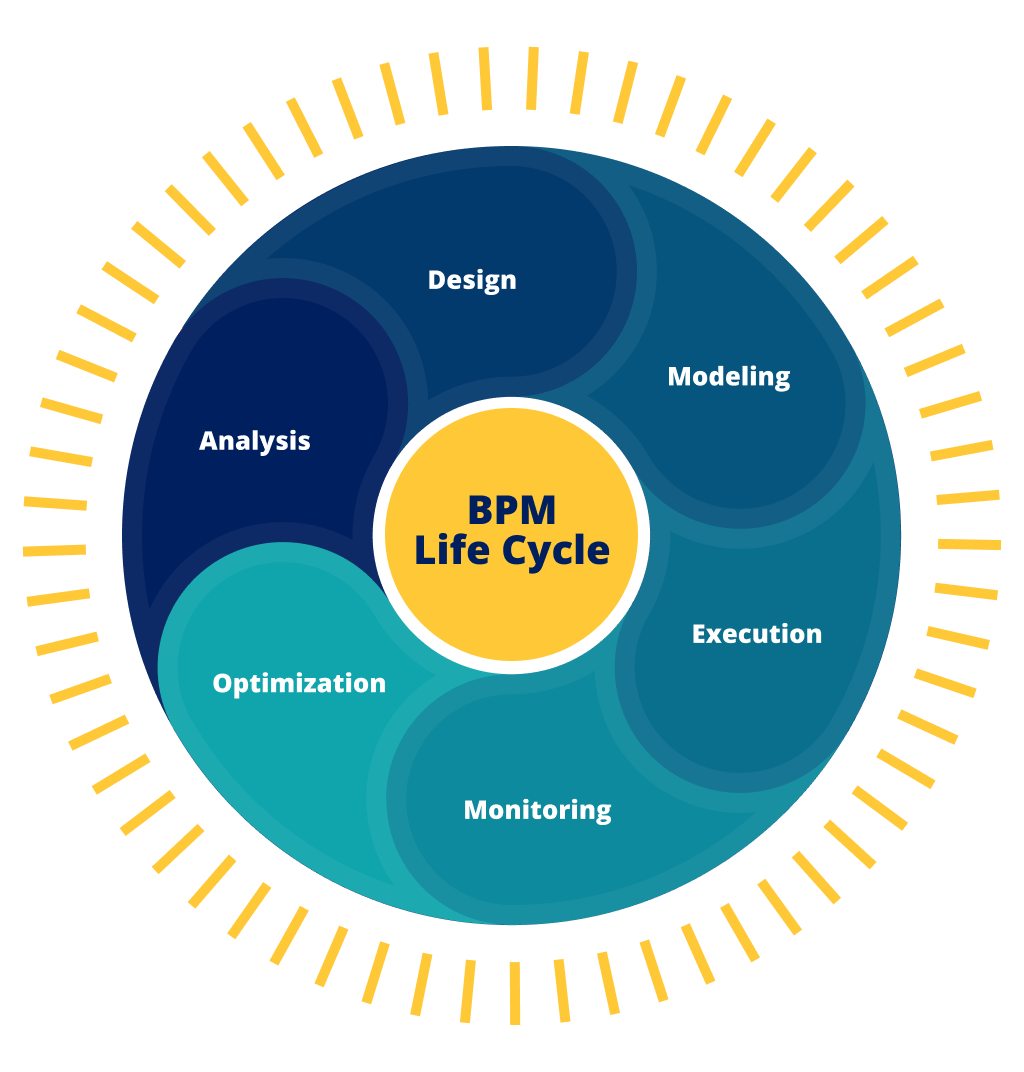
BPMライフサイクルとは
BPMを効果的に導入するには、BPMのライフサイクルを理解することが不可欠です。これは、時間の経過とともにプロセスがどのように特定され、設計され、実行され、改善されるかを示す構造化されたアプローチです。各ステージは、効率的でスケーラブル、かつ適応性の高いビジネスオペレーションを構築する上で重要な役割を果たします。
- 分析:ビジネス要件を満たしたり、パフォーマンスを改善するために作成または最適化できるプロセスやワークフローを発見、特定するために、包括的な分析を行います。
- 設計:人間から人間、システムからシステム、または人間からシステムへのインタラクションを含むプロセス設計を作成します。設計では、エラーの削減と、関連する操作手順やSLAの維持を目標とします。
- モデリング:ソフトウェアツールを使用して、効果的にモデル化を行ってプロセス設計を評価します。プロセス設計の準備ができたら、さまざまな入力値を使用してプロセスの動作を観察します。好ましくない動作が観察されるたびに設計を変更します。
- 実行:ビジネスルール、意思決定、ケースマネージメント、その他の関連テクノロジーでプロセスを自動化します。
- モニタリング:パフォーマンス、エラー、コンプライアンスについてプロセスから収集したレポートデータを活用します。モニタリングにより、企業は実行されたBPMソリューションを対応する設計モデルや関連KPIと比較して評価できます。
- 最適化:モデリングおよびモニタリング段階で収集されたデータを使用して、さらに効率的で好ましい値を導き出すために、改善の余地のあるソリューションの分野を特定します。
BPMコンポーネント
BPMの主要コンポーネントにより、より賢く、より速く、より一貫性のある業務が可能になります。データを活用し、現在のニーズを分析し、その時点で最適な対応を提供することで、インテリジェンスをアクションに変えます。
AIを使用して、顧客ニーズを予測し、インタラクションをパーソナライズし、チャネル全体で体験を簡素化します。
タスクと成果を管理するためのケースを中心に、人間と機械による複雑な作業を最初から最後まで管理します。
複雑なプロセスを自動化します。ルールを設定して、ビジネスアプリケーション内で目標を実行に移します。
事業改善のために、統計をわかりやすいレポートで分析できるようにします。
不正アクセスから保護するためのフレームワークを提供します。パフォーマンスと可用性を低下させる攻撃を防ぎます。
広範で柔軟なコネクター、アダプター、APIサービスを使用して、あらゆるアプリケーションからデータにアクセスします。

BPMの課題と戦略的ソリューション
最新のBPMシステムの導入には依然としていくつかの課題が残っていますが、そのソリューションはより洗練され、戦略的なものへと進化しています。
- 実装の複雑さはBPMのハードルになる可能性があります。パイロットプロジェクトから段階的に導入することで、チームの自信構築、価値の可視化、そして組織全体に導入する前のリスク低減につながります。
- 変更管理は、大きな課題になる可能性があり、従業員は新しいプロセスに抵抗感を持つことが多くあります。成功は、明確なコミュニケーション、強力なトレーニング、導入とユーザビリティを優先する部門横断的なチームにかかっています。
- テクノロジーの統合は困難な場合がありますが、分析、自動化、改善をサポートする柔軟なBPMプラットフォームによって容易になります。Pegaの統合プラットフォームのような最新のソリューションは、システムの統合、サイロ化の解消、プロセスやチャネル間のシームレスな接続の実現に役立ちます。
エージェント型AIによるBPMの強化
エージェント型AIは、目標の理解、行動の自律的な計画・実行、変化への適応を可能にすることで、BPMを強化します。ルールベースのオートメーションとは異なり、複雑さを通してコンテキストや理由を認識、意思決定を行い、経験から学習します。これにより、最小限の人手でアジリティと戦略的価値を実現する、知的で強靭かつ自己最適化するプロセスが実現します。Pega Blueprintは、ビジネス目標と適応的なAI駆動の実行を結びつけるエージェント型ワークフローを、モデル手動で設計できるようにすることで、このビジョンを実現します。
BPMの未来:エージェント型ワークフローの登場
ランドスケープのBPMが進化し続ける中で、最も顕著なトレンドの1つはエージェント型ワークフローへの移行です。これらのワークフローは、タスクの自律的な管理、意思決定、変化する状況への適応を実行できるAIエージェントを活用しながら戦略的な人間の監督と整合しながら機能します。従来のルールベースのシステムとは異なり、エージェント型ワークフローは動的でコンテキストを認識し、インタラクションから学習する能力を備えています。これにより、企業は硬直したプロセスの自動化から、よりインテリジェントで柔軟性と拡張性の高い業務に移行できます。
