Ever wonder how Pega supports the global deployment needs of the largest organizations in the world?
Introduction
Today’s global corporations have multiple lines of business spread across many locations, spanning different business needs. The software that runs your business must meet your needs, including keeping up with your fast-moving, ever-changing global business. It must be flexible, allowing you to quickly configure to meet your business requirements and adapt when those requirements change. The business rules and logic that govern how you operate need to be incorporated seamlessly, such that the software you use to operate your business is a dynamic extension of how you work. You don’t have the time or resources to recreate or duplicate the applications or features you created for one project into another similar project – or to maintain inflexible frameworks to satisfy the complexities regional diversity brings. You need a way to easily move or share functionality seamlessly to achieve your goals.
Pega has been a pioneer in helping global organizations automate the way work gets done. Let’s take a closer look at how we make that possible.
Pega Deployment Manager running on Pega Cloud® supports global deployments for Pega applications, which are built on a globally distributed architecture. Global deployments allow you to deploy applications across production environments distributed around the world, and to reuse applications and “built-ons” to harness the value of Pega Situational Layer Cake™. But before we get to Deployment Manager and how Pega supports the deployment of your global solutions, let’s review the architectural landscape that makes this all possible.
Pega’s Center-out architecture delivers the outcomes you need
The global organizations we work with live in a disparate world – with enterprise and departmental applications that have been acquired or built over time, filling out the landscape of solutions that run the business. As application architectures have evolved, solutions that are built with logic encoded into the different front-end channels users interact with – or built around back-end data sources – have proved brittle and difficult to maintain. Pega recognized these problems early on and builds solutions with a Center-out architecture.
Center-out thinking starts with the intelligence or the decisions you want to make, whether that’s with rules-based systems, statistical AI, or (increasingly) generative AI. This intelligence – whether AI, rules-based, or a mix of the two – operates across all available channels and is consistently enforced to get work done. It goes beyond decisions and captures the necessary automations, workflows, and processes to deliver the outcomes you want. What’s more, it’s expressed in the form of a case, within a defined lifecycle that “understands” the context of the work and is governed by stages and steps through to completion.
Pega Situational Layer Cake architecture speeds development and reuse
One of the primary ways we enforce these consistent outcomes is with the Pega Situational Layer Cake. Our Situational Layer Cake architecture represents Pega’s unique approach to managing complexity and variability in enterprise applications. At its core, it provides a sophisticated system that allows organizations to create a coherent, layered architecture that efficiently handles variations across different business contexts. You can more easily manage enterprise-wide standardization while supporting regional customizations and reuse standard policies and procedures across multiple business units, channels, and geographies.
The Situational Layer Cake effectively balances two competing forces: the desire for reuse to gain economies of scale and consistency with the ability to allow for variations in the process, across geographies, units, products, etc. Application logic built into these layers is dynamically assembled at run-time to reflect the right process, with no need for if-then-else logic. The Layer Cake architecture works across components shared between applications, or even by sharing an entire application between multiple other applications. To save time and reduce development costs, you can reuse elements between your applications by creating and then using “built-on” or “shared” applications. A shared application is built to serve a common need and is consumed by one or many applications in your organization.
At the base layer, you define the logic to be used across the enterprise, for example, the data sources you might need or the enterprise security elements that need to be applied. Above that layer, you define the logic and steps for your specific application – logic unique to that application (for example, retail banking) – that will also use the logic defined at the base level. On top of that, perhaps you have certain product offerings – maybe a lending application with lending-specific needs (for example, documents for underwriting that are required for lending). And on top of that, you might have region-specific rules for your application – things you need to do in certain regions only, perhaps to meet regulatory or compliance needs. You can define as many layers as are practical for your use case – maybe within a region, for example, or other layers that are specific to localities or municipalities for whom unique rules need to be applied.
Now that we’ve laid this relevant backdrop, let’s get back to our core subject:
Deployment Manager
We’ve spent some time talking about the ways Pega efficiently manages application logic with our Center-out architecture and the Situational Layer Cake. With those tools in your bag, how can you effectively deploy complex, reusable solutions across your global application landscape? An important part of deploying and running your applications is your Development Operations (DevOps) process. You need a standardized and best-practice–driven deployment process to deploy predictable, high-quality application releases.
Pega Deployment Manager is a cloud-based solution that automates DevOps workflows. With Deployment Manager, you don’t need third-party tools – you can fully automate your continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) workflows, including application package generation, artifact management, and package promotion to distinct stages in the workflow. Use Deployment Manager to merge branches, apply quality gates, and promote applications across your environments.
Building a reusable application
When you build your application stack, consider how you can meet your business requirements in the most efficient way. For example, when you create an application to review mortgage requests, you can add a built-on application that workers use to review loan requests and then reuse the elements that are relevant to the mortgage cases. (See Adding built-on applications.)
Once you have determined that certain functionalities should be in a built-on application, and created that application, you can use it in other applications. Teams working in different regions might require a shared built-on layer for development and deployment of the applications that they build, which will be deployed to multiple, globally distributed production environments.
Pega Cloud
Speaking of applications, let’s not forget that your primary objective in buying Pega was to solve complex business problems. Your business is not building software – it’s using software to achieve your business objectives. Similarly, you don’t want to spend all your time worrying about the platform your applications are running on – they should just work.
Pega Cloud, Pega’s as-a-Service offering, enables you to focus on achieving the business outcomes you want, while Pega manages secure, reliable, and scalable cloud services that keep your business humming. Pega Cloud helps mitigate risk, accelerate growth, reduce costs, and achieve sustainability targets. With Pega Cloud, your solutions are always-on and ready to scale. You can continuously innovate with access to the most modern Pega solutions, which are seamlessly updated and enhanced automatically.
Ok, now that we’ve reviewed all of that, let’s tie it together.
Global Deployment Manager: Using RTL to deploy a globally distributed application with reusable applications in different regions on Pega Cloud
A Route to Live (RTL) is an industry-standard DevOps pipeline with which you can continuously evolve your work across multiple environments running an application in various stages of development. In practice, an RTL helps you to deliver work rapidly, iterate code more frequently, and verify that the choices you make to establish your solution lifecycle meet business needs and deliver high-quality results. Pega recommends organizing the delivery of application enhancements by using RTLs, so you can include a packaged set of services that align to the functions and stages used to deploy new applications, as well as continuously improve existing ones. For more information, see Establishing a prescriptive Route to Live.
The following use cases show when to deploy across RTLs:
- Teams who work in different and independent RTLs and want to share a built-on layer for development and promotion of their applications.
- Teams who deploy an application across production environments in different regions that target a global customer base.
Sharing a built-on layer
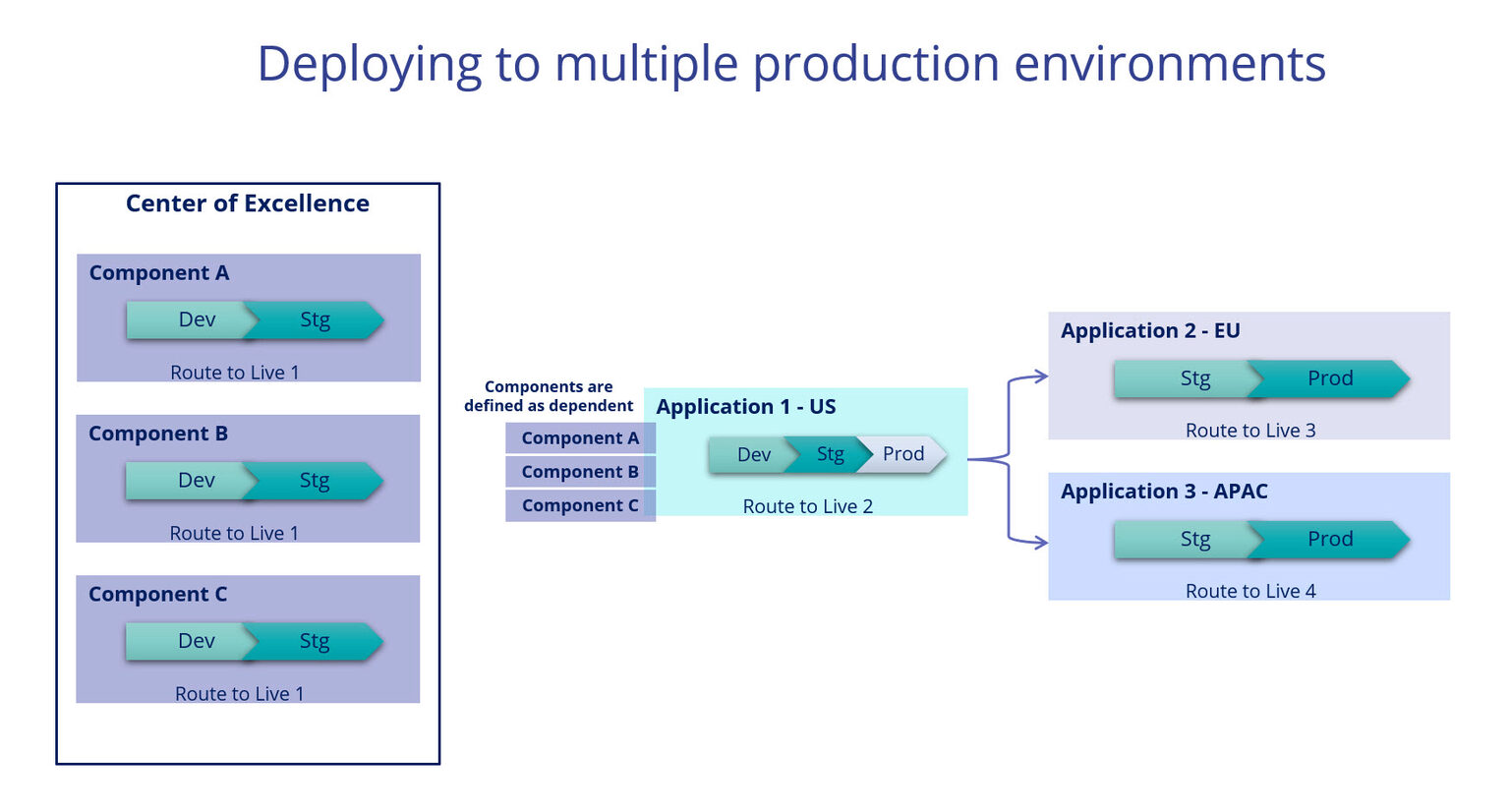
Some clients may have components or even applications which they wish to share across multiple other applications. For example, a bank might have a component or small application that allows users to provide feedback. The bank has different Pega applications which handle mortgages, car loans, and checking-account creation, but after the customer has gone through one of these processes, the bank wants to collect feedback on the customer’s experience with their interaction (mortgage, loan, or checking). So the bank’s center of excellence (COE) creates a component which provides a form for the user to enter feedback. This component sends email to thank the user for their feedback; routes the feedback to the appropriate group; tracks the work done on the feedback; and finally sends another email to the user explaining what the outcome of their feedback was. This component can be added to the end of the processes for the mortgage, car loan, checking account opening, or any other applications the bank is using.
The following example shows the relationship between applications and RTLs:

NOTE: A common repository, such as a COE, is required to allow cross-RTL access. Your COE can create multiple reusable components, which can be defined as dependencies for your applications.

Deploying across different regions
Today’s global corporations have multiple lines of business spread across many locations, spanning different business needs. You may need to access the same application in multiple countries, but due to network latency or compliance regulations, the application must be run in a local region.
Rather than having to manually update applications in different regions, the global deployment feature in Deployment Manager allows you to automatically update all deployments of an application across multiple regions.
In this implementation, called a multi-production deployment, you determine in what region the application will be built and tested. Once you have fully tested the new application (or the update to an existing application) and moved it into production, Deployment Manager will automatically copy the production version of the application into the additional regions. As this new application (or updated application) was already fully tested, you can deploy based on your company’s process; you can choose to deploy the fully tested application (you do not need to move the development and staging versions of the application – just the production application), or you can deploy via a pipeline with additional validations in place.
Summary
Think of the power of the tools we’ve discussed today. Pega’s Center-out architecture and the Situational Layer Cake allow you to capture business rules and logic where they most make sense (removed from the complexity of the front- and back-ends). The elegance of the Situational Layer Cake ensures that you can reuse logic and accommodate for variations across different elements of your business. Tying it all together, Pega Deployment Manager, with its globally aware capabilities, allows you to manifest this technology in the real world, deploying solutions based on this sophisticated and flexible architecture across your far-flung application landscape. And for Pega Cloud clients, all these capabilities are provided free of charge to help you get the most out of your Pega investment.
Our goal is to ensure clients can focus on innovation and drive the business outcomes they need with Pega – seamlessly within their complex application architectures. Interested in learning more? Check out Pega documentation for a detailed review of our global deployment capabilities.
Prerequisites
To support global deployments using the Deployment Manager service on Pega Cloud, the following prerequisites apply:
- Your RTLs must be on the latest version of Pega Cloud (3+) powered by AWS.
- Your applications must use Deployment Manager service for continuous deployments.
- Your RTL environments must be on the PegaDevOpsFoundation application, version 6.3 or higher.

