Workflow management
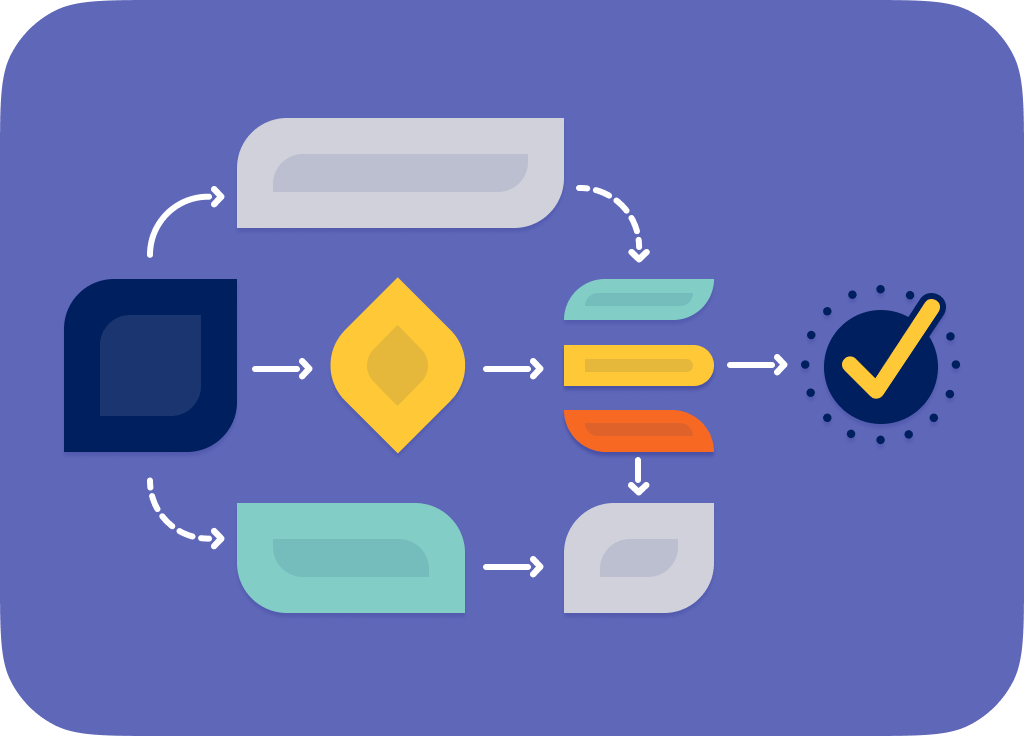
What is workflow management?
Workflow management is the coordination, management, and execution of various tasks and processes within an organization. It involves overseeing the sequence of operations, ensuring that each job is carried out efficiently to achieve a specific goal.
Workflow management makes it possible to drive better outcomes by designing, guiding, and automating every organizational workflow from start to finish for end-to-end visibility. It begins with defining and mapping processes through workflow diagrams and infusing automations to streamline repetitive tasks. Allocating the right resources, monitoring work, and tracking progress all help to ensure efficiency.
What’s the difference between workflow management and workflow automation?
Workflow management
- Involves the end-to-end management of business processes, from mapping and design to execution and optimization
- Is about understanding how different tasks come together to create a process and managing those processes to achieve optimal efficiency
Workflow automation
- Is a component of workflow management focused specifically on using technology to automate individual tasks within a process
- Involves implementing software and tools to carry out repetitive, predictable tasks without human intervention, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing errors

Why is workflow management important?
Enterprise workflow management is not just about improving individual processes; it's about enhancing an enterprise's overall operational health and strategic positioning through intelligent workflows. This makes it critical within an enterprise context.
Benefits of workflow management
- Streamlining operations: Enterprises often have complex operations involving numerous tasks and processes. Workflow management helps streamline these processes, eliminating redundancies and ensuring each step is necessary and efficient.
- Enhancing productivity: Workflow management can involve automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks with technologies like robotic process automation. This enables companies to increase their productivity and empowers their employees to focus on higher-value work.
- Improving consistency and quality control: Standardized workflows ensure consistency in processes and outcomes, which is crucial for maintaining quality standards. This consistency is especially important in enterprises where the scale of operations can lead to variable output.
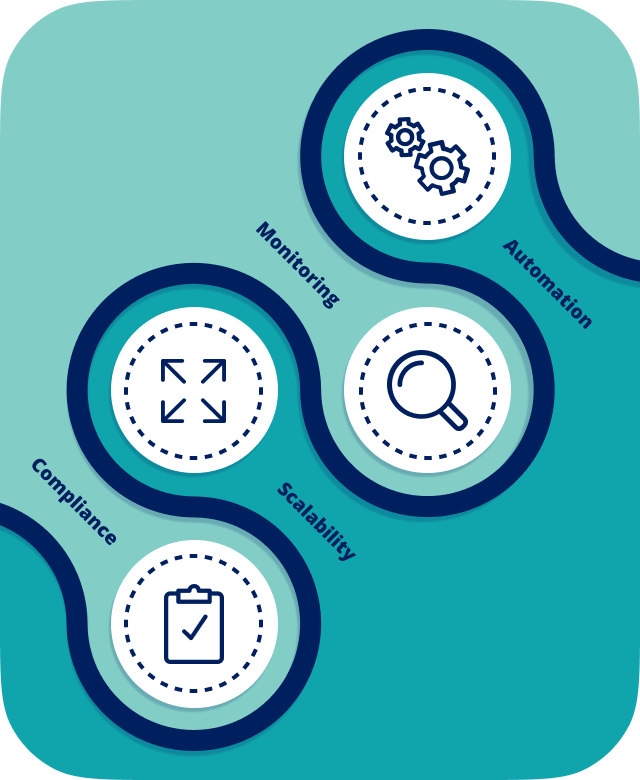
- Offering scalability: As businesses grow, their processes and workflows become more complex. Workflow management systems are scalable, allowing enterprises to adapt and manage increasing volumes of work easily without a proportional increase in errors or inefficiencies.
- Maintaining compliance and risk management: Many enterprises operate in regulatory environments with strict compliance requirements. Workflow management ensures that all processes align with these requirements, reducing legal and financial risks.
How does workflow management work?
Workflow management is a systematic approach to structuring and optimizing the way tasks and processes are carried out in an organization. Let's consider a hypothetical financial services company to illustrate how it works:
- Process identification and mapping: The company maps out key processes, visualizing each step from start to finish. For instance, the loan processing workflow might start with application submission, followed by credit checks, document verification, and finally, loan approval or rejection.
- Automation: The company automates routine tasks such as initial credit checks and document verifications in loan processing, which enhances efficiency and minimizes errors.
- Resource allocation and management: Resources, including skilled staff and technology, are strategically allocated. For instance, experienced personnel might take over complex tasks such as risk assessment.
- Monitoring and tracking: The company employs workflow software to monitor tasks, quickly identifying and addressing any delays. For example, the system might alert managers when a high volume of applications causes a slowdown in credit checks.
- Performance analysis and optimization: The company conducts regular analysis of workflow efficiency. For example, if it identifies a recurring delay in the risk assessment stage of loan processing, it might streamline the process or add more resources to that stage to improve efficiency.
- Communication and collaboration enhancement: Workflow tools improve interdepartmental communication, ensuring smooth coordination and timely client updates. For instance, the loan processing team could easily update the customer service team on the status of an application, enabling them to provide timely information to clients.
- Adherence to compliance and standards: Workflow management tools can be designed to ensure all processes comply with financial regulations, such as checking that each loan application has undergone all legal and compliance steps before approval.
- Flexibility and scalability: Workflow management systems are adaptable and scalable, allowing the company to adjust to growth and market changes while maintaining efficient and compliant operations.

Drive consistent outcomes, deliver meaningful results, and be ready for what comes next.

Challenges of workflow management
Implementing workflow management in an organization does bring its own set of challenges, including:
- Employee resistance: Adopting new processes and technologies can create resistance from employees who may be reluctant to change established routines.
- Integration complexity: Integrating workflow management systems with existing IT infrastructure can be complex, leading to delays in the implementation process.
- Data security and privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of data, particularly when handling sensitive information, is a critical concern that requires careful attention.
- Risk of oversimplification: There is a risk of oversimplifying processes, potentially overlooking the nuances of specific tasks in an attempt to streamline workflows.
How to mitigate challenges
With care and consideration, companies can mitigate these challenges and harness the benefits of workflow management processes. This requires a three-pronged approach:
- Practical training: Providing practical instruction to employees can help them adapt to new processes and technologies more effectively.
- Effective communication: Clear and transparent communication helps address concerns, manage expectations, and foster a smooth transition to workflow management.
- Flexible systems: A flexible and customizable workflow management system can adapt to the unique needs and complexities of an organization's workflow.
What are some use cases for workflow management?
Workflow management can enable a variety of industries to manage the delicate balance of efficiency and quality. The key is tailoring the workflow management system to the specific needs and challenges of the industry and the organization. Let's explore what this might look like in practice in real industries.
Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare providers utilize workflow management for patient care coordination, from admission to discharge. This includes managing patient records, scheduling appointments, and streamlining the communication between various departments. Automating administrative tasks allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, workflow management can optimize production lines. This includes automating inventory management, scheduling equipment maintenance, and coordinating supply chain operations. Workflow management helps reduce downtime, improve product quality, and ensure timely delivery of goods.
Information technology
IT departments use workflow management to handle software development, issue tracking, and resolution. Workflow management helps prioritize tasks, allocate resources effectively, and maintain clear communication among team members. Automated workflows ensure timely updates and releases, bug tracking, and efficient resolution of IT issues.

Deciding on and scaling a workflow management platform
Choosing a workflow management platform requires a thorough assessment of an organization's needs, processes, and future scalability requirements. It's crucial to select a platform that fits the current workflow and is adaptable as the business grows. Key considerations include:
- Ease of integration with existing systems
- User friendliness
- Customization capabilities
- Robustness in handling data security
To scale a workflow management platform, it's essential to review and update the workflow processes regularly. You should also ensure that the platform can handle increased loads and provide ongoing training and support to users.
What is the future of workflow management?
The future of workflow management is heavily intertwined with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI is increasingly used to optimize workflows by analyzing large volumes of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend improvements.
AI-powered tools can automate more complex decision-making processes, and AI is even enhancing workflow automation capabilities by enabling more sophisticated and adaptive systems that can learn and evolve. Integrating AI into workflow management promises greater efficiency and productivity and holds the potential for more innovative and intelligent process optimization in the future.
Getting started with agentic AI
Traditional workflow management focuses on structuring and optimizing tasks to improve efficiency. However, the integration of agentic AI transforms these workflows into dynamic, self-optimizing systems.
Pega's platform leverages agentic AI to enhance workflow management by:
- Autonomous task execution: AI agents can independently manage and complete tasks, reducing manual oversight and accelerating process completion.
- Real-time adaptability: Workflows can adjust dynamically to changing data and conditions, ensuring optimal performance even in volatile environments.
- Intelligent decision-making: Agentic AI enables workflows to make informed decisions based on contextual data, improving accuracy and outcomes.
By embedding agentic AI into workflow management, Pega empowers organizations to move beyond static process automation, embracing a future where workflows are intelligent, responsive, and aligned with evolving business needs.
